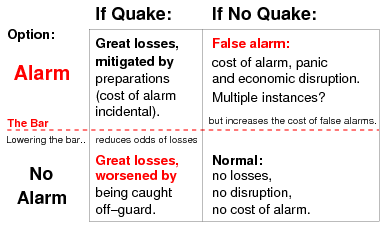
Read this, make notes on what is happening
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2014/jun/08/why-we-are-losing-a-world-of-languages
Tuesday 11 July 2017
Thursday 6 July 2017
Resistance to cultural diffusion
This news clip demonstrates the tension created by the cultural diffusion of American Corporate Capitalism, not only with indigenous societies in developing countries, but also in developed countries such as France.
Summarise what is happening here:
Summarise what is happening here:
Wednesday 5 July 2017
Social & environmental impacts of hyper-urbanisation
Recently we've explored the global shift in manufacturing (offshoring), and now, in services too (outsourcing).
As a result of these two processes, emerging countries have experienced astonishingly rapid economic growth. We studied the environmental impacts of these changes in China, but we need to also look at India.
The best resource for this is here, 'Slumming it' with Kevin McCloud. Create a mindmap with two main branches: social and environmental. There is of course overlap between the two. Watch both parts
As a result of these two processes, emerging countries have experienced astonishingly rapid economic growth. We studied the environmental impacts of these changes in China, but we need to also look at India.
The best resource for this is here, 'Slumming it' with Kevin McCloud. Create a mindmap with two main branches: social and environmental. There is of course overlap between the two. Watch both parts
Wednesday 28 June 2017
Y12 - international migration - low-skilled labourers and elites
The clips from yesterday's lesson. Please make notes on what is happening and why
Thursday 22 June 2017
Y12 - globalisation and megacity growth
Please use this link to complete the handout on megacity growth
BBC - megacities interactive
Then highlight the different statements into whether they are for (a) developed or (b) emerging/developing megacities
BBC - megacities interactive
Then highlight the different statements into whether they are for (a) developed or (b) emerging/developing megacities
Friday 16 June 2017
Y12 - impacts of globalisation on ecology and biodiversity
For Tuesday:
Research and make notes on these three links. They focus on different impacts of China's rapid rise.
Infrastructure
https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2016/may/10/china-pearl-river-delta-then-and-now-photographs
Housing and social problems
https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2017/mar/20/changsha-changing-mao-growth-housing-services
Pollution and chemical leaks
https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2017/may/23/city-exploded-china-growth-tianjin-disaster-inevitable
For each of the links, please explore the interactive/time-lapse maps and also watch the drone footage for the last link
Research and make notes on these three links. They focus on different impacts of China's rapid rise.
Infrastructure
https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2016/may/10/china-pearl-river-delta-then-and-now-photographs
Housing and social problems
https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2017/mar/20/changsha-changing-mao-growth-housing-services
Pollution and chemical leaks
https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2017/may/23/city-exploded-china-growth-tianjin-disaster-inevitable
For each of the links, please explore the interactive/time-lapse maps and also watch the drone footage for the last link
Thursday 8 June 2017
Y13 - FOR TOMORROW
Learn this model - AT LEAST THE SUBHEADINGS and 1 or 2 of the topics. Reference it - (Blaikie et al, 1994)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:PAR_model.pdf
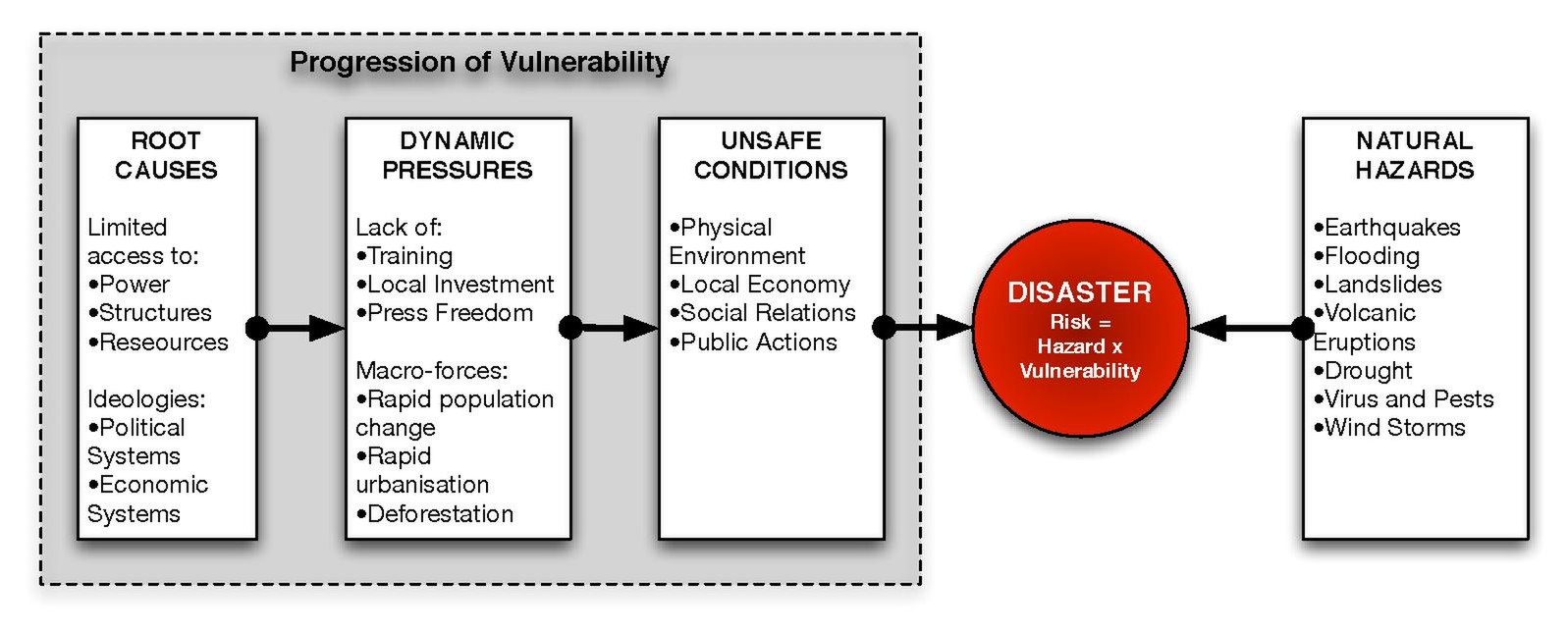
Then, learn all the main facts for our case studies.
Tohuku 2011, Japan,
Nevado Del Ruiz 1985, Colombia
Eyaffajokul 2010, Iceland
Pinatubo, 1991, Philippines
Haiti, 2010
Mt St Helens, 1980, USA
Italy 2015/16
Indian Ocean Tsunami, 2004
Memorise the names of sources - at least 5.
Memorise the names of websites & organisations - eg. "Corruption Perception Index, Transparency International - NGO".
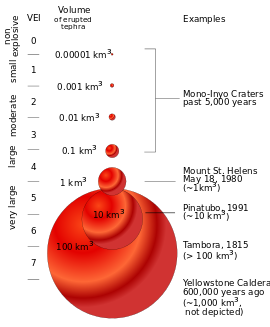
Learn the VEIs of Pinatubo, Nevado Del Ruiz, and Eyafajjallokul
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volcanic_Explosivity_Index#/media/File:VEIfigure_en.svg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:PAR_model.pdf

Then, learn all the main facts for our case studies.
- Plate tectonic cause
- year
- magnitude (Richter & VEI)
- social cost (no. dead)
- economic cost
- environmental cost (eg. 2 million trees [Mt St Helens])
Tohuku 2011, Japan,
Nevado Del Ruiz 1985, Colombia
Eyaffajokul 2010, Iceland
Pinatubo, 1991, Philippines
Haiti, 2010
Mt St Helens, 1980, USA
Italy 2015/16
Indian Ocean Tsunami, 2004
Memorise the names of sources - at least 5.
Memorise the names of websites & organisations - eg. "Corruption Perception Index, Transparency International - NGO".
Learn the VEIs of Pinatubo, Nevado Del Ruiz, and Eyafajjallokul
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volcanic_Explosivity_Index#/media/File:VEIfigure_en.svg

Sunday 28 May 2017
Y12 - Globalisation - half term work
The half term work comes in two parts:
1. To complete the work we began on 'switched off' and 'switched on' places around the world, answer this question. Write a detailed paragraph (half a side) with 2 examples for each of the four factors.
"Analyse the physical, political, economic, and environmental reasons why some locations are 'switched off' from globalisation".
To reach the higher levels, remember to pick holes in your own points. So, just after having mentioned Nepal and how it's landlocked, you then do a big "however" and mention Switzerland, and try to explain why, in this case, being landlocked is not a problem.
Use the KOF map of globalisation to find some examples.
2. Download the PDF file from this link Global Shift PDF
a) define the global shift
b) identify the causes/what has enabled it to happen
c) mindmap the impacts on China and India
1. To complete the work we began on 'switched off' and 'switched on' places around the world, answer this question. Write a detailed paragraph (half a side) with 2 examples for each of the four factors.
"Analyse the physical, political, economic, and environmental reasons why some locations are 'switched off' from globalisation".
To reach the higher levels, remember to pick holes in your own points. So, just after having mentioned Nepal and how it's landlocked, you then do a big "however" and mention Switzerland, and try to explain why, in this case, being landlocked is not a problem.
Use the KOF map of globalisation to find some examples.
2. Download the PDF file from this link Global Shift PDF
a) define the global shift
b) identify the causes/what has enabled it to happen
c) mindmap the impacts on China and India
Monday 22 May 2017
Y12 - measuring globalisation
Read p.162-163. Mindmap the ways the KOF index and the A T Kearney Index measure globalisation.
Which is a better measure? Explain your decision.
Next, use this KOF map to mindmap/create a table showing the physical, environmental, political, economic factors that explain 'switched on' and 'switched off' places around the world. Use examples!
Eg: (under 'physical') Nepal - mountainous - lack of internet infrastructure; landlocked - no ports for access to trade routes.
Which is a better measure? Explain your decision.
Next, use this KOF map to mindmap/create a table showing the physical, environmental, political, economic factors that explain 'switched on' and 'switched off' places around the world. Use examples!
Eg: (under 'physical') Nepal - mountainous - lack of internet infrastructure; landlocked - no ports for access to trade routes.
Wednesday 5 April 2017
Y13 - Thursday 6th April
For today's lesson we aim to complete a Unit 2 mock (the paper I gave you yesterday). The aim is to complete this paper in the double lesson - remember that the real exam gives you just 1 hr 15 min.
We need to aim for speed and accuracy in our writing, hence why we are using the essay plans we created overnight.
When you have finished these, please leave them on my desk.
Best of luck
Friday 31 March 2017
Unit 4 - factors that affect the EFFECTIVENESS OF managing hazards
Unit 4 - factors that affect the EFFECTIVENESS OF managing hazards
Read this link and make notes on it
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog030/node/379
Here are some case studies to consider:
PLACE
Remoteness/accessibility: Nevado del Ruiz, Colombia, 1985, 2007 Solomon Islands earthquake
Hotspots: Mt Merapi, Indonesia
Eruption types: Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, Peléan, Plinian, Surtseyan, Submarine, Subglacial, Phreatic eruptions (for these, a specific eruption case study might not be necessary), super-volcano (caldera) - Campi Flegrei
Earthquake types: blind-thrust, mega-thrust, interplate & intraplate, deep-focus quakes shallow quakes - Haiti 2011; deep - Chile 2010, aftershocks (Nepal 2015)
PEOPLE
Population density & distribution: 1964 Alaskan earthquake vs 2010 Haiti earthquake, Kamchatka Peninsula, Campi Flegrei, Naples,
Coasts compared with landlocked places: Indian Ocean tsunami 2004, Nepal 2015
Demographics: Japan 2011 (ageing populations) https://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2011/03/japans-earthquake-and-the-hazards-of-an-aging-population/72892/
Culture & beliefs: Indian Ocean Tsunami 2004 (Andaman islands) http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/south_asia/4181855.stm
Disadvantaged groups: Banda Aceh (2004) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_Aceh_Movement
Education: Indian Ocean Tsunami (2004) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V0s2i7Cc7wA
Employment: farmers in the Phillippines, fishermen in the Indian Ocean Tsunami, tourists (2004 Tsunami
POWER - TO FOLLOW
Read this link and make notes on it
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog030/node/379
Here are some case studies to consider:
PLACE
Remoteness/accessibility: Nevado del Ruiz, Colombia, 1985, 2007 Solomon Islands earthquake
Hotspots: Mt Merapi, Indonesia
Eruption types: Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, Peléan, Plinian, Surtseyan, Submarine, Subglacial, Phreatic eruptions (for these, a specific eruption case study might not be necessary), super-volcano (caldera) - Campi Flegrei
Earthquake types: blind-thrust, mega-thrust, interplate & intraplate, deep-focus quakes shallow quakes - Haiti 2011; deep - Chile 2010, aftershocks (Nepal 2015)
PEOPLE
Population density & distribution: 1964 Alaskan earthquake vs 2010 Haiti earthquake, Kamchatka Peninsula, Campi Flegrei, Naples,
Coasts compared with landlocked places: Indian Ocean tsunami 2004, Nepal 2015
Demographics: Japan 2011 (ageing populations) https://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2011/03/japans-earthquake-and-the-hazards-of-an-aging-population/72892/
Culture & beliefs: Indian Ocean Tsunami 2004 (Andaman islands) http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/south_asia/4181855.stm
Disadvantaged groups: Banda Aceh (2004) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_Aceh_Movement
Education: Indian Ocean Tsunami (2004) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V0s2i7Cc7wA
Employment: farmers in the Phillippines, fishermen in the Indian Ocean Tsunami, tourists (2004 Tsunami
POWER - TO FOLLOW
Capitalism: Indian Ocean Tsunami 2004 http://www.naomiklein.org/shock-doctrine/resources/part7/chapter19/thailand-tsunami-survivors-group
Democracy vs dictatorship: Chile vs Iran http://www.slate.com/articles/news_and_politics/fighting_words/2010/03/long_live_democratic_seismology.html
Transparency vs corruption: Haiti 2010, Chile 2010 https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/2010-07-15/disaster-politics
The role of NGOs: http://nacla.org/news/ngos-and-business-poverty-haiti
Local communities: Nepal 2016 http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/southasia/2016/05/03/community-participation-should-be-at-the-heart-of-nepals-post-earthquake-reconstruction-process/
https://www.hands.org/localvolunteers/
https://www.hands.org/localvolunteers/
Government agencies: FEMA (federal emergency management agency) http://disasterphilanthropy.org/issue-insight/fema/
Political instability (links to Banda Aceh 2004): http://www.dw.com/en/how-political-instability-affected-nepals-disaster-preparedness/a-18411259
Thursday 30 March 2017
Y13 - Unit 3 work, Thursday 30th March
Friday 24 March 2017
3D modelling - San Andreas Fault zone
Use this to explore how the SA fault is monitored, using 3D GIS modelling
http://www.southerncaliforniaweatherforce.com/2016/06/21/breaking-the-code-models-predict-next-rupture-point-of-san-andreas-fault-earthquake/
USGS - San Andreas zoning
http://www.southerncaliforniaweatherforce.com/2016/06/21/breaking-the-code-models-predict-next-rupture-point-of-san-andreas-fault-earthquake/
USGS - San Andreas zoning
Sunday 19 March 2017
Y13 - for Wednesday 22nd March
Y13s - for Wednesday - please complete FOUR questions from section A of Unit 3 - two options from two papers. Choose which mock you prefer. We will then peer mark and prepare model answers for these.
Eg: answer BOTH the 10 and 15 marker questions from TWO sections in one paper (eg. bridging the development gap AND Biodiversity under threat). Repeat with another mock.
Lastly, at the top of the paper, write how many minutes it took you to answer each. Use the circle essay plan if you need to.
Eg: answer BOTH the 10 and 15 marker questions from TWO sections in one paper (eg. bridging the development gap AND Biodiversity under threat). Repeat with another mock.
Lastly, at the top of the paper, write how many minutes it took you to answer each. Use the circle essay plan if you need to.
Friday 17 March 2017
Thursday 9 March 2017
Y13 - Unit 4 - research tasks, Friday 10th March
Hello everybody, please ensure you are up to date with the following in your research portfolio:
- Theories of plate tectonics
- Key definitions
- Tectonic hazards - type (event profiles) & global distribution
- plate boundaries/margins
- associated features (rift valleys, ocean trenches, hotspot volcanoes)
- characteristics of each - hazard type, lava type
- Physical impacts
- extrusive landforms
- intrusive landforms
- Human impacts - range of case studies (6 case study profiles, including Park model for each)
- Responses to tectonic hazards
- please find and use the powerpoint on the shared area that has a wide range of techniques and methods of managing earthquakes & volcanoes
- Players involved - research the different groups involved in hazard management - identify: (a) the scale that it operates at; (b) its role and function; (c) it's impact in reducing mortality and disaster prevention
- Future of tectonic hazards - choose a range of different hazards
- Identify areas most at risk in the future because of population growth and unsustainable development
- assess the benefits and costs of different management approaches (in a table?)
The last two topics - response and the future - probably need more attention than the others.
Also, go back through your work, ensuring that you have made a note of the reference (name of website, search term) for all of your material.
Thursday 23 February 2017
Y13 - UNIT 4 - TECTONICS - research tasks
Hi all - tomorrow I have booked C151 for you.
We have now covered the following things in our research portfolio:
- theories of plate tectonics
- physical processes
- extrusive & intrusive landforms
- Case study profiles (including the PARK model for all 6) for a variety of different case studies
If any of these things are incomplete, they must be completed
We now need to spend a week researching the human impacts of tectonic hazards. You will have done some of this when creating the case study profiles.
Look at p.259-264 in the textbook. Spend about 4 hours researching the variation in the impacts and what causes these variations.
Please make sure in your research that you are writing down the references of the sites/books you use.
Saturday 18 February 2017
Energy security - Unit 3
Please read this article, make sure you understand the key points from it
http://www.independent.co.uk/environment/climate-change/renewable-energy-investment-developed-world-developing-world-ren21-report-a7058436.html
http://www.independent.co.uk/environment/climate-change/renewable-energy-investment-developed-world-developing-world-ren21-report-a7058436.html
Wednesday 15 February 2017
UNIT 4 - understanding risk
Please study this graphic. This shows how risk is calculated. Print a copy from this website World Risk Index 2016 and illustrate this with example. Find 5 countries that are at completely different points along the worldriskindex spectrum (at the bottom of the graphic), and bullet point the reasons why. Remember from AS - exposure to natural hazard concerns the frequency and the magnitude of hazards. The vulnerability concerns levels of development and so on.
How do we present/display this? Mindmap? Table? You decide
Friday 10 February 2017
UNIT 4 - Geographical research - for Hollie & others who missed today's lesson
1. 30 minutes: ensure you have diagrams/annotations/notes on the following landforms:
• Batholiths
• Sills
• Dykes
• Faults
• Rift valleys
• microfracturing
(include photo examples of each)
2. 1 hr: Create a notes page on the Parks model. Print, stick, annotate.
3. 5 hours: half term: create case study profiles for 7 tectonic hazards
2. 1 hr: Create a notes page on the Parks model. Print, stick, annotate.
3. 5 hours: half term: create case study profiles for 7 tectonic hazards
Friday 3 February 2017
UNIT 4 - GEOGRAPHICAL RESEARCH - ***IMPORTANT***
Please work through this presentation on slideshare, about
- theory of plate tectonics
- evidence for it
- essentials of oceanography & paleogeography
Some will be familiar; some will not
Please add the appropriate information to your research portfolio
Thursday 19 January 2017
Coastal Management - 4 case studies
You are to create a presentation on 4 case studies:
1. Happisburgh, Norfolk
2. Maldives
3. Namibia
4. Chittagong, Bangladesh
For the last 2 it is slightly harder to find research material. Your presentation slides can only have a title/subtitle. No other words permitted.
Try using these links
http://www.nacoma.org.na/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227604641_Conservation_and_management_of_the_Bangladesh_coastal_ecosystem_Overview_of_an_integrated_approach
http://www.academia.edu/2349449/Coastal_zone_management_Status_of_Bangladesh
For each case study you must examine, and present:
(a) physical processes (geology, how erosion is happening)
(b) what pressures there are on this coastline (population, urbanisation, economic interests)
(c) how the coastline is being managed (hard/soft engineering; ICZM)
(d) what conflicts there are between different players
Thursday 12 January 2017
Tectonics - useful weblinks
Unit 4 – Tectonics
research - useful links for physical causes/tectonic theories
http://www.geo.cornell.edu/hawaii/220/PRI/PRI_PT_home.html
Tectonics from Cornell University
https://www.usgs.gov/products/data-and-tools/real-time-data
US Geological Survery - real-time data on natural hazards
http://www.see.leeds.ac.uk/structure/dynamicearth/
Leeds University Dynamic Earth site
http://www.vulkaner.no/v/volcan/vulkinfo2.html
Volcanic hazards
http://www.nationalgeographic.com/features/04/forcesofnature/forces/earthquakes.html
National Geographic - tectonic hazards
http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/index.html
PBS - animation library
Geology.com –
fascinating website about tectonic hazards
http://geology.com/earthquakes/
Earthquakes
http://geology.com/volcanoes/
Volcanoes
Continental Rift
System
http://nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/rift-valley/
Information about the East African Rift Valley
Friday 6 January 2017
Typhoon Haiyan - why were the effects so severe?
This was our case study. To answer this question: "examine the factors that affect the severity of coastal flooding” we had to consider Typhoon Haiyan, in the Philippines, and also Cyclone Sidr in Bangladesh (in the textbook).
There are two main themes that run through this idea of "severity" (how bad it is). One is the physical factors to do with the typhoon itself, and the other, larger issue is to do with human factors such as the levels of development.
There are two main themes that run through this idea of "severity" (how bad it is). One is the physical factors to do with the typhoon itself, and the other, larger issue is to do with human factors such as the levels of development.
Watch this documentary and make notes on BOTH the physical and human factors. Then write the essay.
Tuesday 3 January 2017
Factors contributing to coastal flooding
Y12 - for today. Please create an A3 revision/summary sheet for the work on Bangladesh. Specifically, the section that focuses on the impacts of cyclone Sidr. Then please look at the impacts of storm surges in the UK.
Pages 134-137
Pages 134-137
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)